肝脏是药物代谢的重要器官,是机体进行生物转化的主要场所,含有参与药物代谢Ⅰ相代谢和Ⅱ相代谢的各种酶。UGT家族是人体内仅次于CYP450家族的第2大药物代谢酶。UGTs介导的葡萄糖醛酸化反应是多种化合物的基本清除机制,这些化合物包含内源性化合物、环境致癌物和临床药物,其原理是UGTs催化葡萄糖醛酸与异生物质的极性基团(例如羟基,硫醇,羧基或胺)结合,使其水溶性增加,促进其向排泄器官的运输,然后通过胆汁、尿液或粪便从机体中排出。
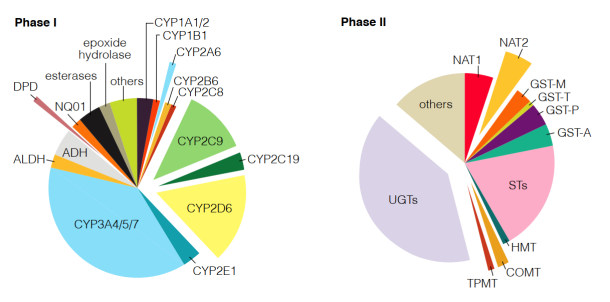
Polymorphic drug-metabolizing enzymes
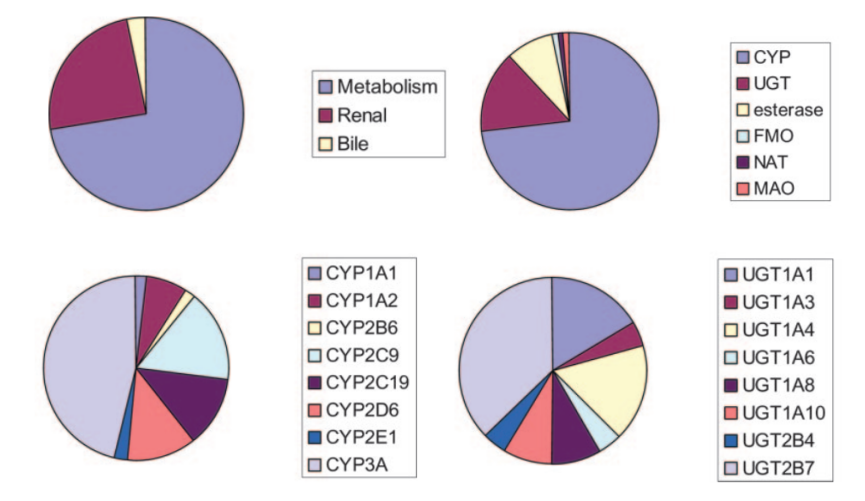
Clearance mechanisms for the top 200 drugs prescribed in the United States in 2002.1
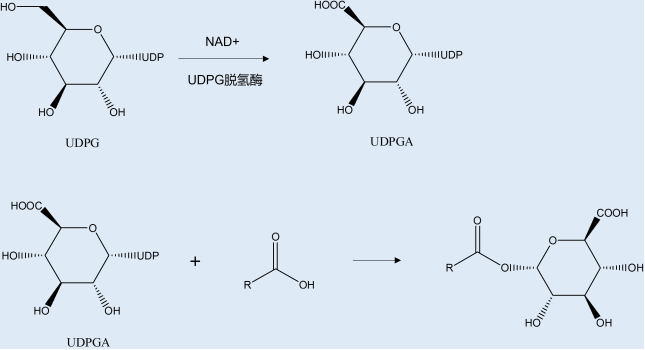
Phase II metabolic process
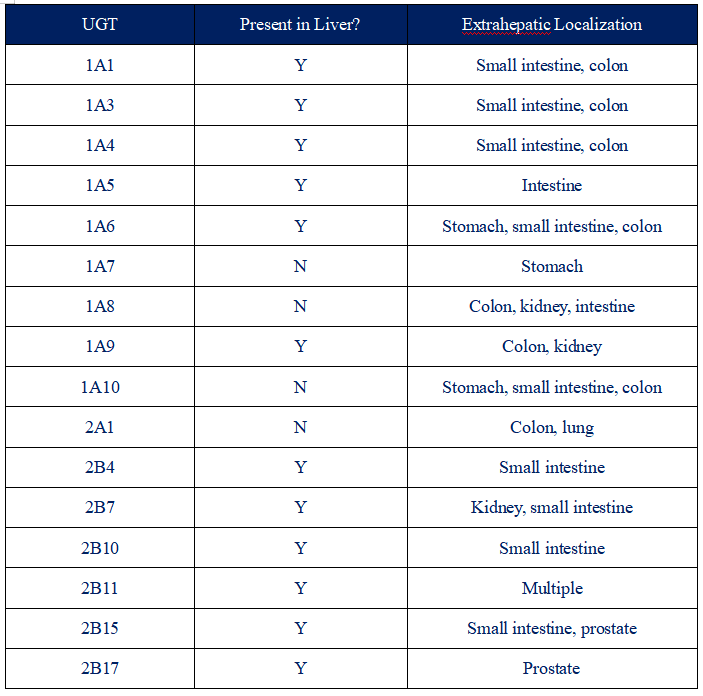
UGT是一类位于内质网的膜蛋白,UGT根据核苷酸序列的相似性分为2个家族,UGT1和UGT2,两者又进一步分为3个亚家族:UGT1A,UGT2A及UGT2B。UGTs分布非常广泛,在肝脏、肾脏、小肠、结肠、胃、肺、上皮、睾丸、乳腺和前列腺中均有表达。其中UGTs表达最丰富的组织是肝脏,其次是肾脏和胃肠道(胃、小肠和结肠)2-6。
General Summary of the Tissue Distribution of UGT Isoforms7-10
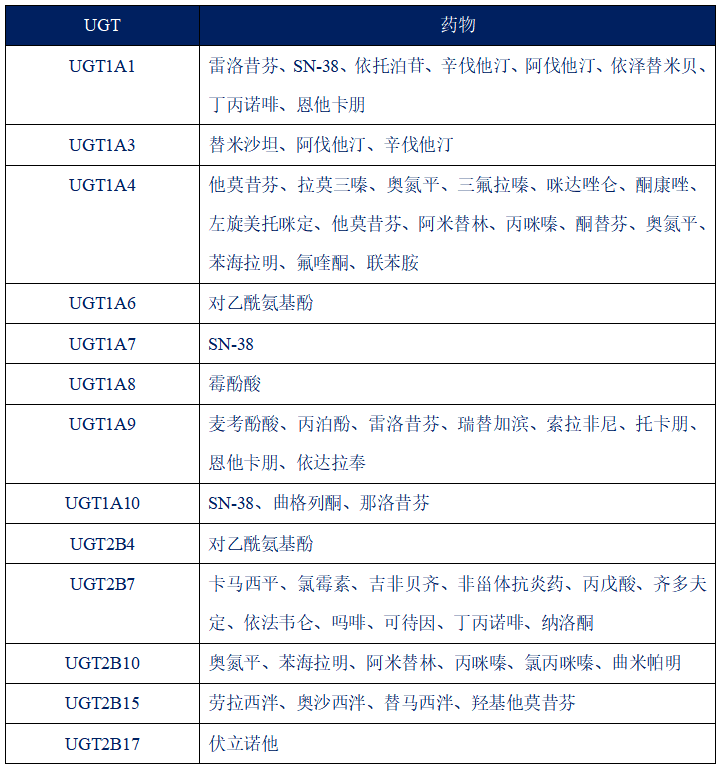
临床上有约35%的药物经UGT代谢。比如,对乙酰氨基酚是广泛使用的解热镇痛临床常用药物,在人体内的清除途径之一就是需要依赖UGTs的葡萄糖醛酸化消除11。伊立替康是目前治疗转移性结直肠癌最有效的化疗药物之一,在体内首先经羧酸酯酶水解转化为细胞毒性更强的7-乙基-10-羟基喜树碱(SN-38),SN-38在体内的清除途径是葡萄糖醛酸化,经UGT(1A1等)代谢为葡萄糖醛酸产物(SN-38G)避免不良反应的发生12。
UGT代谢相关的药物
UGTs是一类遗传性差异发生频率很高的代谢酶,研究证明UGT基因多态性的影响药物代谢及临床应用。例如UGT1A1,因为它在内源性产物胆红素、雌激素、黄酮类化合物及其他药物的葡萄糖醛酸化中起重要作用,而UGT1A1的多态性可引起胆红素水平升高,导致吉尔伯特综合征或更为严重的Criglar-Najar综合征。另外,
UGT也介导激素类、胆汁酸等其他内源性物质的葡萄糖醛酸化,若UGTs的功能受损对其代谢造成影响。
UGT在药物代谢中发挥着重要作用,如果服用具有UGTs抑制的药物或食物后,会影响药物代谢酶介导的药物清除速度,进而影响其血药浓度,导致临床不良反应的发生。比如,苯巴比妥、苯妥英钠在与对乙酰氨基酚联用时,会抑制对乙酰氨基酚葡萄糖醛酸化酶的活性,影响对乙酰氨基酚的正常代谢,导致其在体内的蓄积,增加患者肝毒性的发生率。当氟康唑与齐多夫定共同服用时,氟康唑可通过抑制UGT2B7酶的活性进而抑制了齐多夫定的葡萄糖醛酸代谢,可使齐多夫定表观清除率降低47.6% 13。
UGT家族其在药物代谢中的作用和临床药物-药物相互作用而备受关注,现在正成为药物研发关注的重点,包括UGT1A3、UGT1A4、UGT1A6、UGT1A9、UGT2B7等。因此药品监管部门建议,将UGT抑制作为体外药物-药物相互作用(DDI)包的一部分进行评估,以确定是否需要进行临床DDI研究。
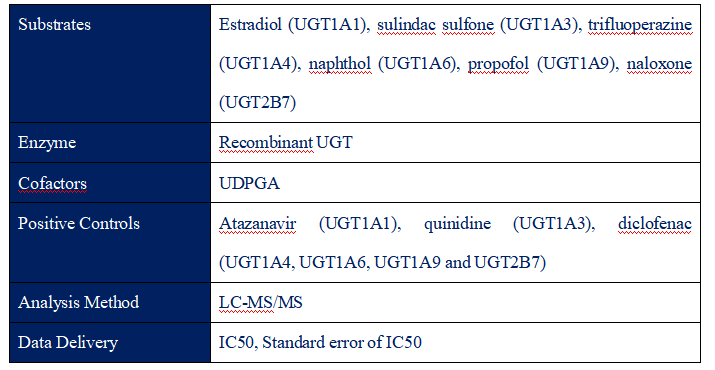
UGT inhibition是爱思益普的体外实验ADMET服务内容之一。
UGT inhibition protocol
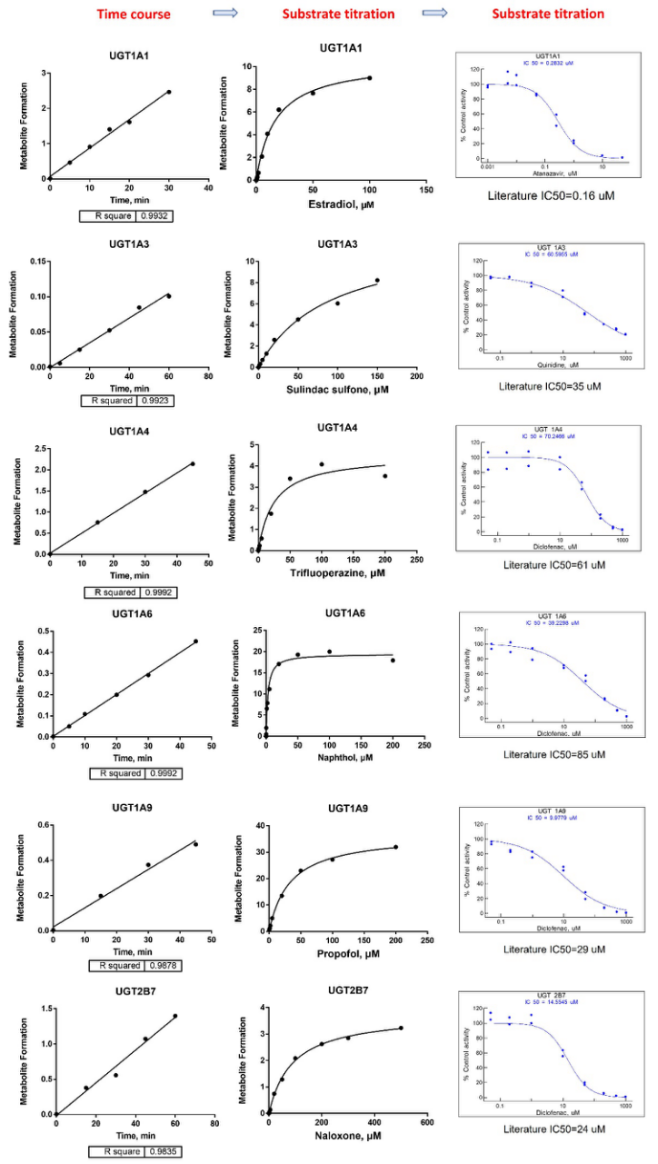
爱思益普具有经验丰富的DMPK团队,建立了新药研发中临床前期ADMET与PK相关实验。体外ADME实验包括药物溶解度实验、Log
D、Log
P实验、肝微粒体和肝细胞代谢、抑制和诱导实验、PPB血浆蛋白结合(HTD和超离)实验、Caco2/PAMPA实验、Transporter等实验。体内PK实验包括啮齿类的大小鼠PK实验非啮齿类比格犬的PK实验、急性毒性实验、毒代实验等,支持多种溶媒的使用、多种给药方式给药、多种组织取材等。ICE可以提供定制化的体内体外相关实验,更好的为客户提供药代动力学服务,助力新药研发。
结合早期靶点验证与机理研究的平台、酶学和细胞学的筛选平台、成药性评价的ADMET平台、PK/PD的分析平台、谱学筛选平台(kinase
panel, safety panel, cell panel,
etc.)等,爱思益普可以更好的为药物研发的团队高效地提供药物构效关系测试,加速中国新药研发项目的进程。
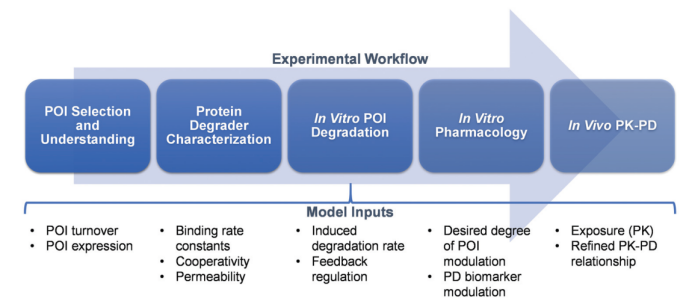
A proposed translational PK–PD roadmap for protein degrader therapeutics
(Bartlett, D. W. and A. M. Gilbert (2022). Chem Soc Rev 51(9): 3477-3486.)
1
Williams JA, Hyland R, Jones BC, et al. Drug-drug interactions for
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates: a pharmacokinetic explanation
for typically observed low exposure (AUCi/AUC) ratios. Drug Metab
Dispos. 2004 Nov;32(11):1201-8.2
Rowland A, Miners JO, Mackenzie PI. The UDP-glucuronosyltransferases:
their role in drug metabolism and detoxification. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 2013 Jun;45(6):1121-32.3
Knights KM, Miners JO. Renal UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and the
glucuronidation of xenobiotics and endogenous mediators. Drug Metab Rev.
2010 Feb;42(1):63-73.4
Gaganis P, Miners JO, Brennan JS, et al. Human renal cortical and
medullary UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs): immunohistochemical
localization of UGT2B7 and UGT1A enzymes and kinetic characterization of
S-naproxen glucuronidation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007
Nov;323(2):422-30.5
Gaganis P, Miners JO, Brennan JS, et al. Human renal cortical and
medullary UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs): immunohistochemical
localization of UGT2B7 and UGT1A enzymes and kinetic characterization of
S-naproxen glucuronidation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007
Nov;323(2):422-30.6
Kiang TK, Ensom MH, Chang TK. UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and clinical
drug-drug interactions. Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Apr;106(1):97-132.7
Tukey RH, Strassburg CP. Human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases:
metabolism, expression, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
2000;40:581-616.8
Strassburg CP, Kneip S, Topp J, et al. Polymorphic gene regulation and
interindividual variation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity in
human small intestine. J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 17;275(46):36164-71.9
Rowland A, Miners JO, Mackenzie PI. The UDP-glucuronosyltransferases:
their role in drug metabolism and detoxification. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 2013 Jun;45(6):1121-32.10
Rowland A, Miners JO, Mackenzie PI. The UDP-glucuronosyltransferases:
their role in drug metabolism and detoxification. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 2013 Jun;45(6):1121-32.11
Linakis MW, Cook SF, Kumar SS, et al. Polymorphic Expression of UGT1A9
is Associated with Variable Acetaminophen Glucuronidation in Neonates: A
Population Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacogenetic Study. Clin
Pharmacokinet. 2018 Oct;57(10):1325-1336.12
Wang L, Chan CEL, Wong AL, et al. Combined use of irinotecan with
histone deacetylase inhibitor belinostat could cause severe toxicity by
inhibiting SN-38 glucuronidation via UGT1A1. Oncotarget. 2017 Jun
20;8(25):41572-41581.13
Uchaipichat V, Winner LK, Mackenzie PI, et al. Quantitative prediction
of in vivo inhibitory interactions involving glucuronidated drugs from
in vitro data: the effect of fluconazole on zidovudine glucuronidation.
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Apr;61(4):427-39.
地址:北京市通州区科创十三街与经海路交汇处
电话:010-67809840
邮箱:services@ice-biosci.com
官网:http://www.ice-biosci.com/
 来源:本站
来源:本站
 浏览量:15338
浏览量:15338